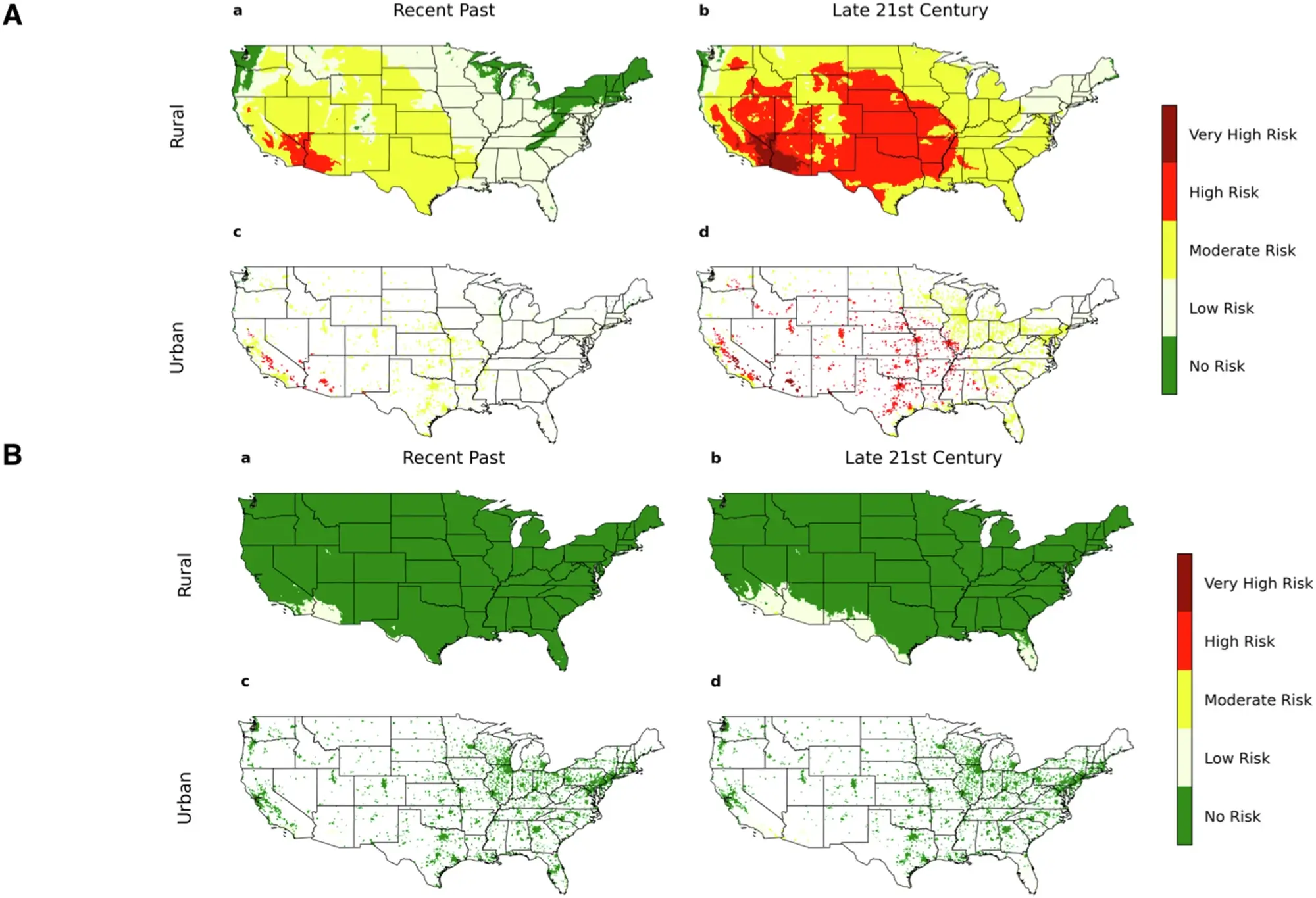
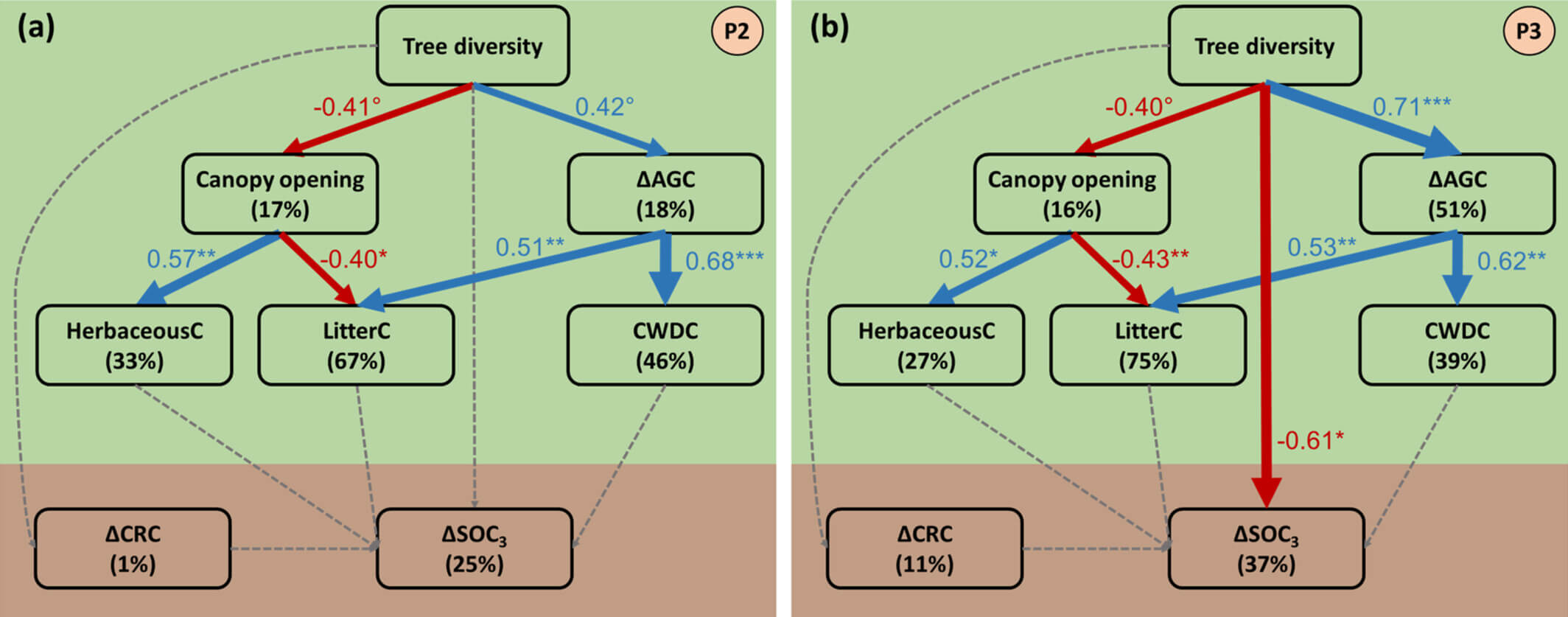
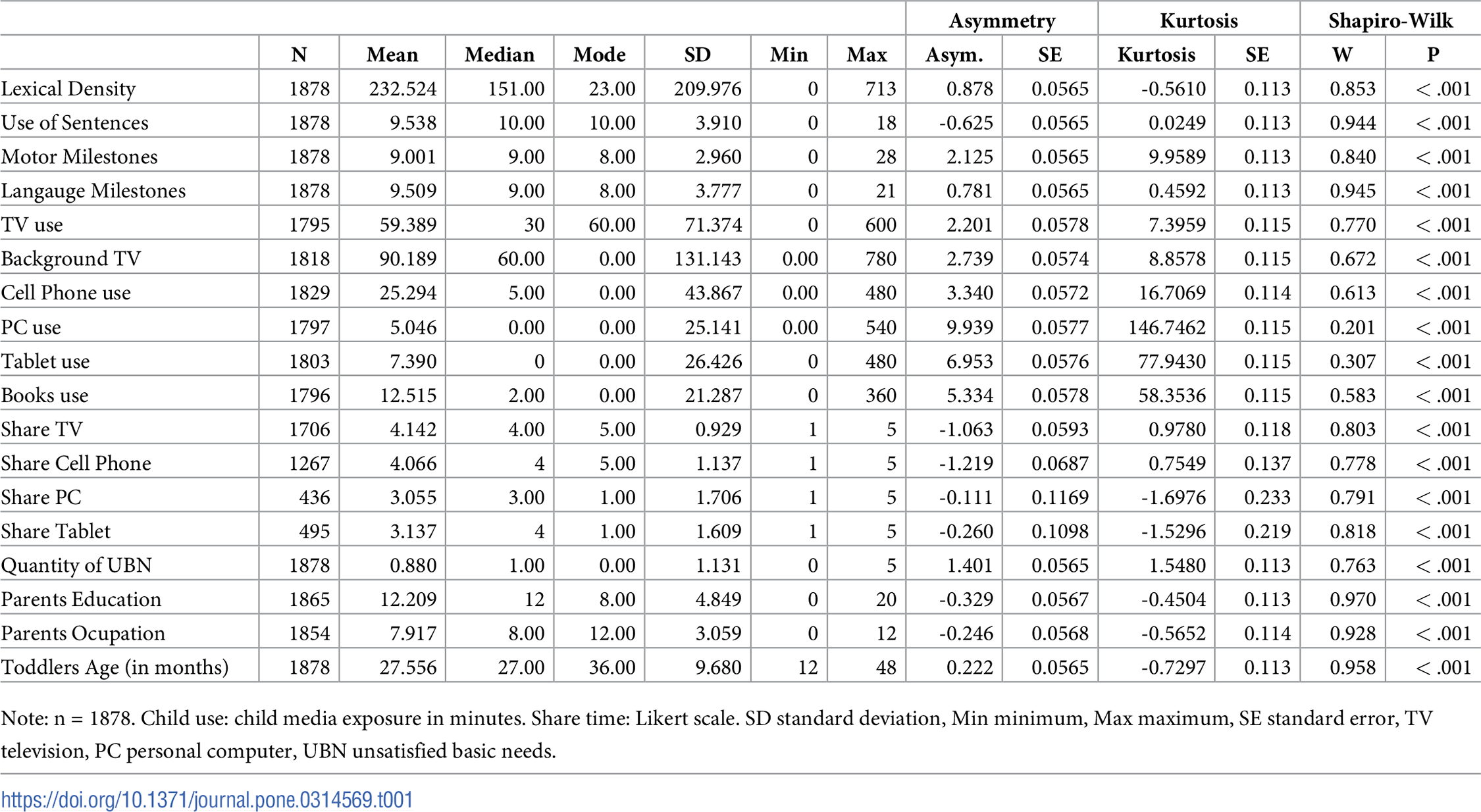
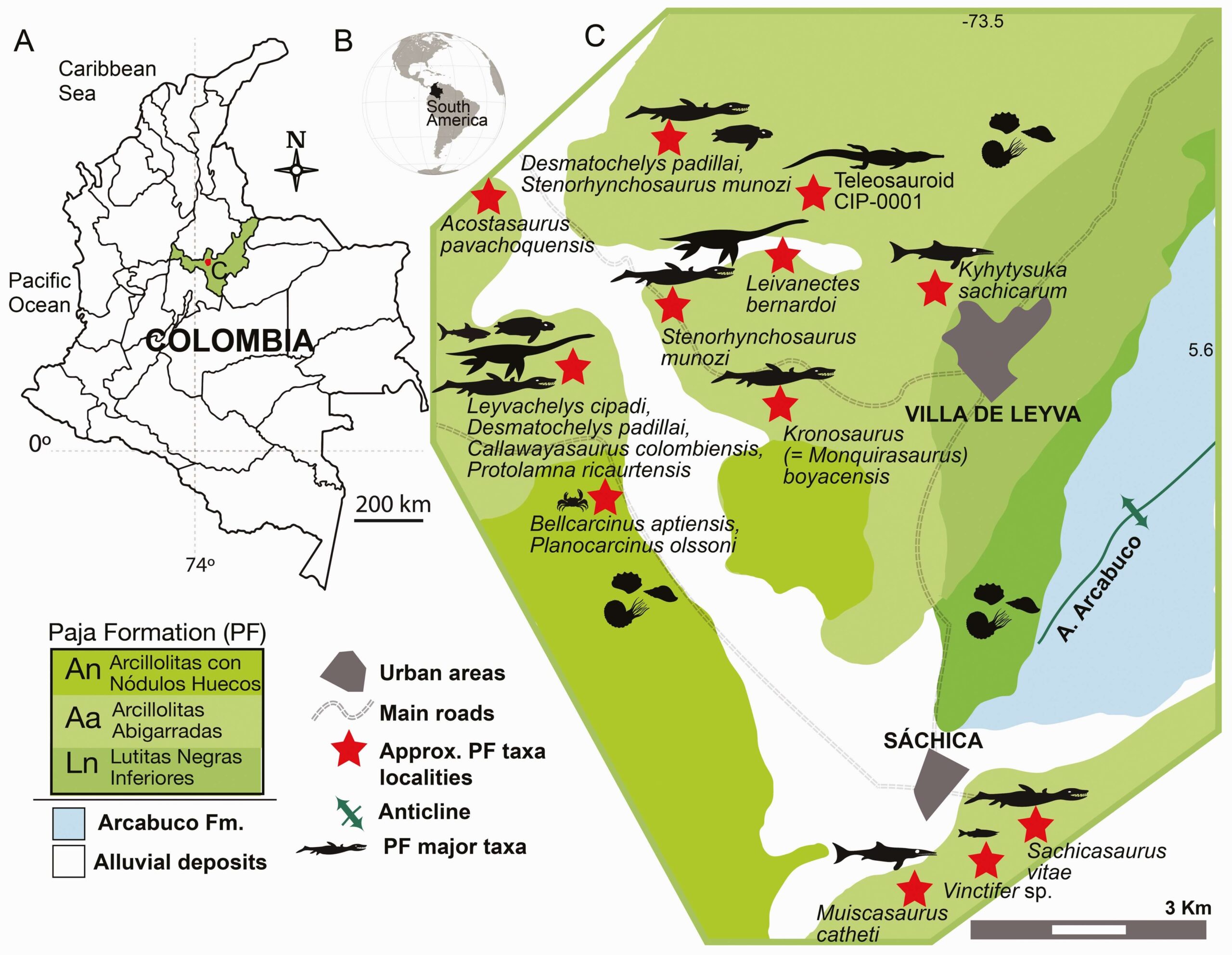
Solubility Calculations
Calculate solubility (S) from the solubility product constant (Ksp) or determine Ksp from solubility using this calculator.
What is Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)?
The solubility product constant (Ksp) represents the equilibrium concentration of ions in a saturated solution of a sparingly soluble salt. It is calculated using the dissociation equation of the compound:
General Formula:
AₘBₙ ⇌ mAⁿ⁺ + nBᵐ⁻
Ksp is expressed as:
\[ K_{sp} = (m^m \cdot n^n) \cdot S^{(m+n)} \]
Where:
- Ksp = Solubility product constant
- S = Solubility (mol/L or M)
- m, n = Stoichiometric coefficients from the dissociation equation
How to Calculate Solubility from Ksp?
To find S (mol/L):
- Write the dissociation equation of the compound.
- Identify the m and n values.
- Use the formula:
\[ S = \left( \frac{K_{sp}}{m^m \cdot n^n} \right)^{\frac{1}{m+n}} \]
- Solve for S.
Example Calculation (Solubility from Ksp)
For PbSO₄ ⇌ Pb²⁺ + SO₄²⁻, we have m = 1, n = 1:
Ksp = S²
If Ksp = 1.77 × 10⁻⁸, then:
S = √(1.77 × 10⁻⁸) = 1.33 × 10⁻⁴ M
How to Calculate Ksp from Solubility?
To find Ksp:
- Write the dissociation equation.
- Identify m and n.
- Use the formula:
\[ K_{sp} = (m^m \cdot n^n) \cdot S^{(m+n)} \]
Example Calculation (Ksp from Solubility)
For Ag₂SO₄ ⇌ 2Ag⁺ + SO₄²⁻, with m = 2, n = 1:
Ksp = (2² * 1¹) * S³ = 4S³
If S = 1.33 × 10⁻⁴ M, then:
Ksp = 4 × (1.33 × 10⁻⁴)³ = 9.41 × 10⁻¹²