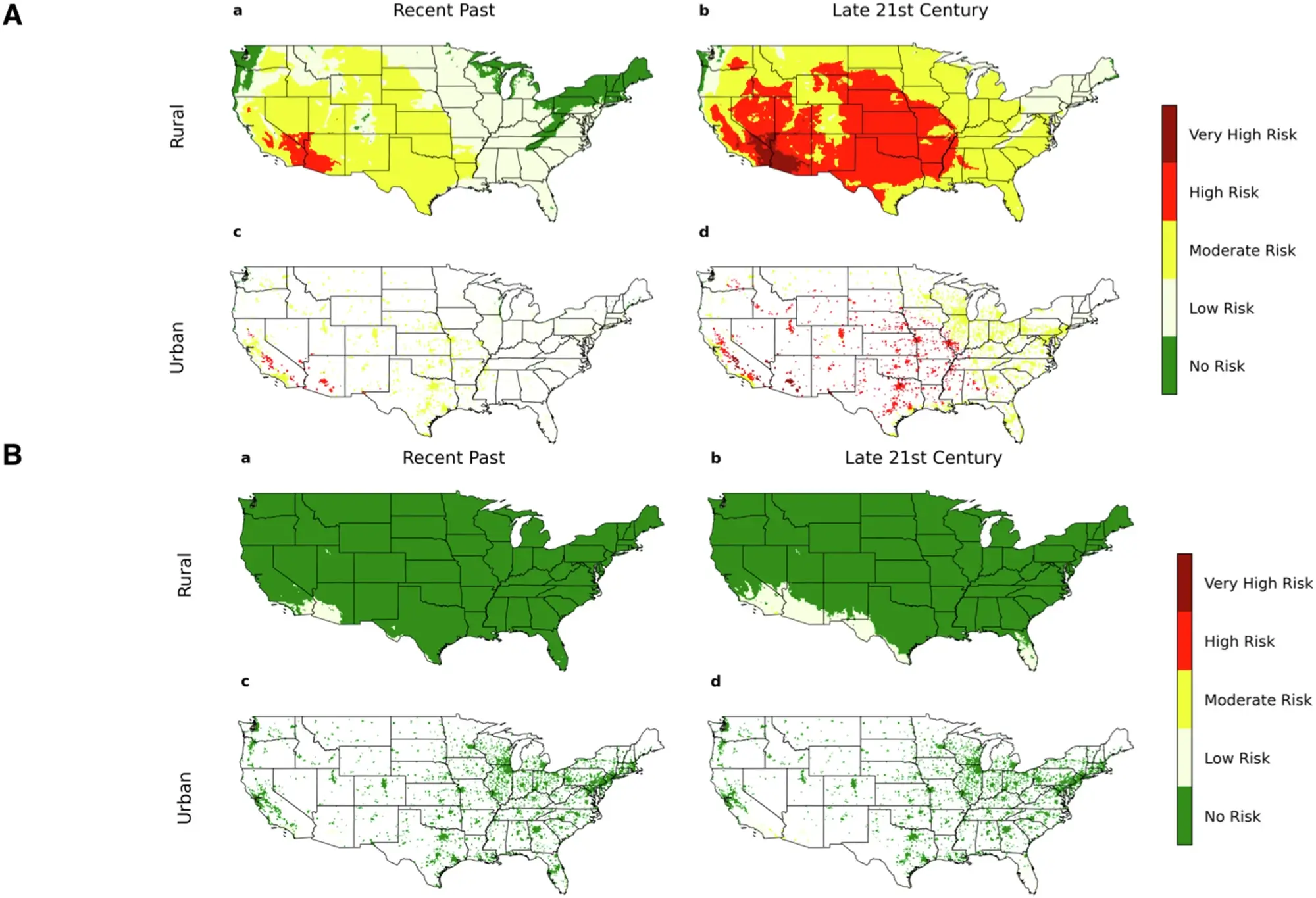
How to Convert Moles to Liters and Liters to Moles at STP
At STP, conversions are straightforward because 1 mole of an ideal gas always equals 22.4 liters. No complicated formulas—just simple multiplication or division!
Moles to Liters (Gas at STP)
To find the volume in liters, multiply the number of moles (n) by 22.4 L/mol:
Volume (L) = Moles (n) × 22.4 L/mol
Liters to Moles (Gas at STP)
To find the number of moles, divide the volume (L) by 22.4 L/mol:
Moles (n) = Volume (L) ÷ 22.4 L/mol
Plug your values into our calculator and get instant, accurate results!
Moles to Liters Conversion Examples (Gas at STP)
Check out this table of sample conversions from moles to liters at STP:
| Moles (n) | Volume (L) = n × 22.4 |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | 11.2 L |
| 1.0 | 22.4 L |
| 2.0 | 44.8 L |
| 5.0 | 112.0 L |
| 10.0 | 224.0 L |
Liters to Moles Conversion Examples (Gas at STP)
Here’s a table converting liters to moles for gases at STP:
| Volume (L) | Moles (n) = L ÷ 22.4 |
|---|---|
| 11.2 | 0.5 mol |
| 22.4 | 1.0 mol |
| 44.8 | 2.0 mol |
| 89.6 | 4.0 mol |
| 224.0 | 10.0 mol |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does STP mean in gas calculations?
STP stands for Standard Temperature and Pressure, defined as 0°C (273 K) and 1 atm. At these conditions, 1 mole of an ideal gas occupies 22.4 liters.
2. Why is 22.4 liters used for 1 mole of gas?
The value 22.4 L/mol comes from the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) at STP. It’s the molar volume of an ideal gas under standard conditions.
3. Can this calculator work for gases not at STP?
No, this calculator is designed only for gases at STP (0°C, 1 atm). For other conditions, you’d need to adjust using the ideal gas law.
4. How do I know if my gas is ideal?
Ideal gases follow the ideal gas law perfectly. Most real gases (like O₂ or N₂) behave ideally at STP, so this calculator works well for them.
5. What’s the volume of 3 moles of gas at STP?
Multiply 3 moles by 22.4 L/mol: 3 × 22.4 = 67.2 liters. Try it with our calculator to confirm!