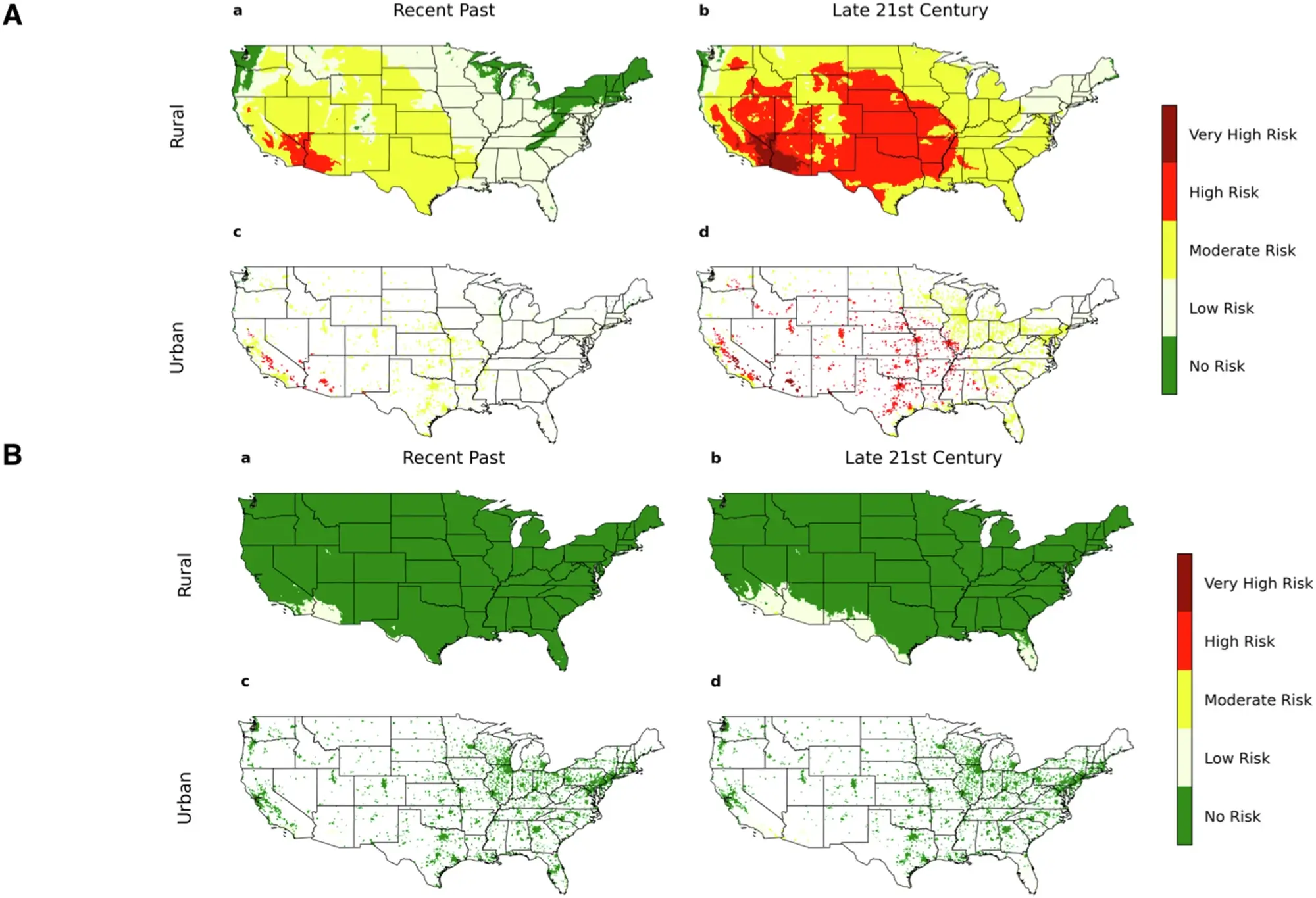
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates the pH of a solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base (or a weak base and its conjugate acid) to the pKa of the acid (or pKb of the base) and the ratio of their concentrations. It simplifies pH calculations in buffer solutions.
Concept
Weak acids don’t completely dissociate in water. They reach an equilibrium described by the acid dissociation constant, Ka:
HA ⇌ H⁺ + A⁻
Ka = [H⁺][A⁻] / [HA]
Where:
- HA is the weak acid
- A⁻ is its conjugate base
- [H⁺] is the hydrogen ion concentration
- [HA] is the concentration of the weak acid
- [A⁻] is the concentration of the conjugate base
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is derived from this equilibrium expression by taking the negative logarithm of both sides and rearranging:
pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
Where:
- pH is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration (-log[H⁺])
- pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (-logKa)
Related Posts
Example Practice Questions
- Question: Calculate the pH of a solution containing 0.1 M acetic acid (CH₃COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10⁻⁵) and 0.1 M sodium acetate (CH₃COONa). Solution:
- Sodium acetate is the conjugate base of acetic acid.
- pKa = -log(Ka) = -log(1.8 x 10⁻⁵) = 4.74
- pH = pKa + log([CH₃COONa]/[CH₃COOH]) = 4.74 + log(0.1/0.1) = 4.74
- Question: What is the ratio of [A⁻]/[HA] for a solution with a pH of 5.0 if the pKa of the weak acid is 4.0? Solution:
- pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
- 5.0 = 4.0 + log([A⁻]/[HA])
- log([A⁻]/[HA]) = 1.0
- [A⁻]/[HA] = 10¹ = 10
- Question: A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 0.2 M ammonia (NH₃, Kb = 1.8 x 10⁻⁵) and 0.2 M ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl). Calculate the pOH and pH of the solution. Solution:
- Ammonium chloride is the conjugate acid of ammonia.
- pKb = -log(Kb) = -log(1.8 x 10⁻⁵) = 4.74
- pOH = pKb + log([NH₄Cl]/[NH₃]) = 4.74 + log(0.2/0.2) = 4.74
- pH = 14 – pOH = 14 – 4.74 = 9.26
- Question: You need to prepare a buffer with a pH of 7.4. You have a weak acid with a pKa of 7.0. What ratio of conjugate base to weak acid is required? Solution:
- pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
- 7.4 = 7.0 + log([A⁻]/[HA])
- log([A⁻]/[HA]) = 0.4
- [A⁻]/[HA] = 10⁰.⁴ = 2.51 (approximately)
- Question: A solution contains 0.15 M benzoic acid (C₆H₅COOH, Ka = 6.3 x 10⁻⁵) and 0.10 M sodium benzoate (C₆H₅COONa). Calculate the pH. Solution:
- Sodium benzoate is the conjugate base of benzoic acid.
- pKa = -log(Ka) = -log(6.3 x 10⁻⁵) = 4.20
- pH = pKa + log([C₆H₅COONa]/[C₆H₅COOH]) = 4.20 + log(0.10/0.15) = 4.02