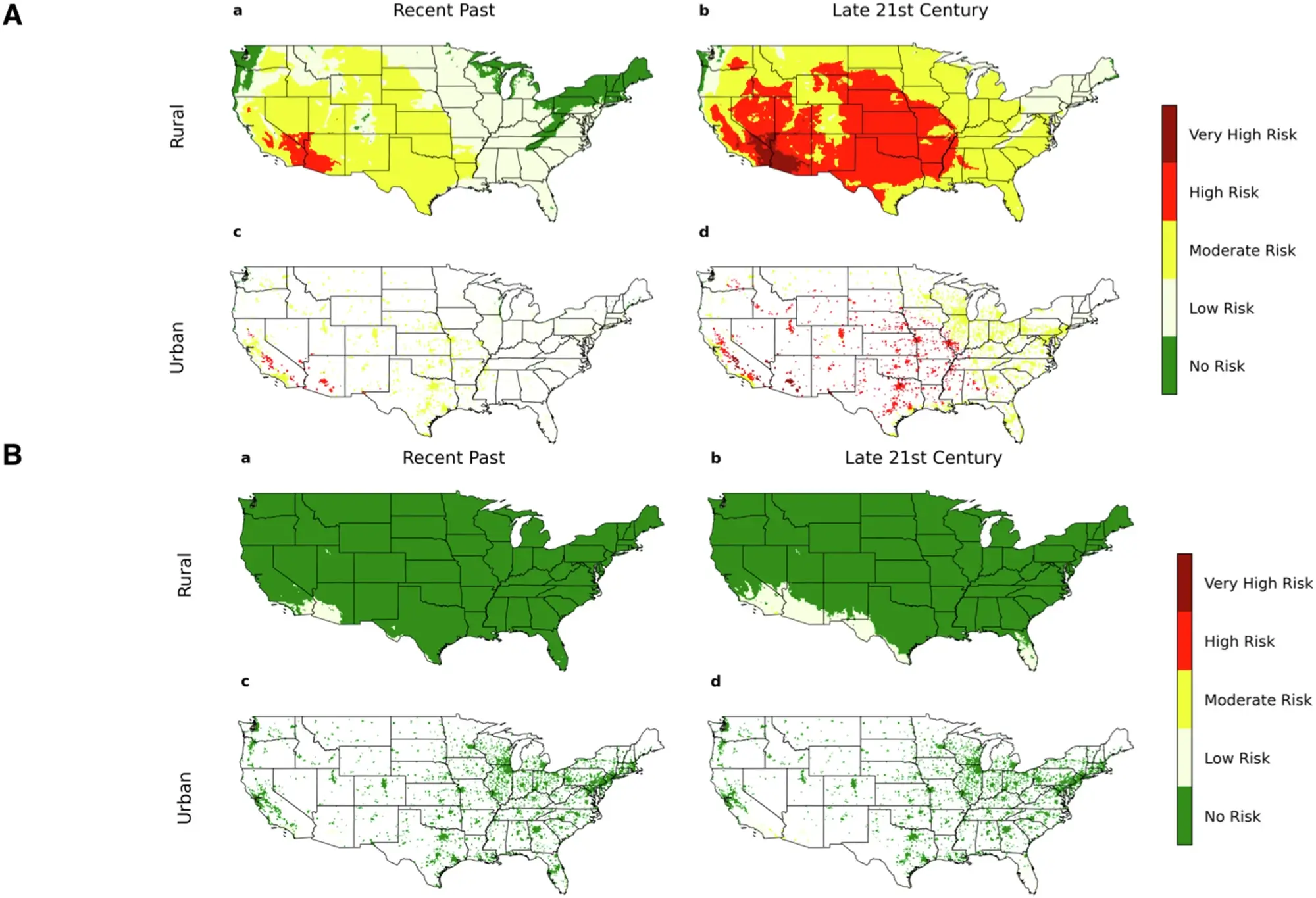
Functional Group
A functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that determines its chemical properties and reactivity. Functional groups define how molecules interact in chemical reactions.
| Functional Group | Formula | Example | Name Example |
| Alkane | C-C | CH₄ | Methane |
| Alkene | C=C | C₂H₄ | Ethene |
| Alkyne | C≡C | C₂H₂ | Ethyne |
| Alcohol | -OH | C₂H₅OH | Ethanol |
| Haloalkane | -X (F, Cl, Br, I) | CH₃Cl | Chloromethane |
| Aldehyde | -CHO | CH₃CHO | Ethanal |
| Ketone | -CO- | CH₃COCH₃ | Propanone |
| Carboxylic Acid | -COOH | CH₃COOH | Ethanoic acid |
| Ester | -COO- | CH₃COOCH₃ | Methyl ethanoate |
| Amine | -NH₂ | CH₃NH₂ | Methylamine |
| Amide | -CONH₂ | CH₃CONH₂ | Ethanamide |
| Nitrile | -CN | CH₃CN | Ethanenitrile |
| Phenol | -OH (attached to benzene) | C₆H₅OH | Phenol |
Functional Groups & Their Naming Suffixes
| Functional Group | Suffix | Example Compound | IUPAC Name |
| Alcohol (-OH) | -ol | CH₃CH₂OH | Ethanol |
| Carboxylic Acid (-COOH) | -oic acid | CH₃COOH | Ethanoic acid |
| Aldehyde (-CHO) | -al | CH₃CH₂CHO | Propanal |
| Ketone (-CO- within chain) | -one | CH₃COCH₃ | Propanone |
| Ester (-COO- between groups) | -oate | CH₃COOCH₃ | Methyl ethanoate |
| Amine (-NH₂) | -amine | CH₃CH₂NH₂ | Ethylamine |
| Amide (-CONH₂) | -amide | CH₃CONH₂ | Ethanamide |
| Ether (-O- between groups) | No specific suffix | CH₃OCH₃ | Dimethyl ether |
| Alkene (C=C) | -ene | H₂C=CH₂ | Ethene |
| Alkyne (C≡C) | -yne | HC≡CH | Ethyne |
Functional Groups Worksheet
Section A: Matching Functional Groups to Their Names
Match each functional group in Column A with its name in Column B.
| Column A: Functional Group | Column B: Functional Group Name |
| -OH | 1. Aldehyde |
| -COOH | 2. Alkene |
| -CHO | 3. Alcohol |
| C=C | 4. Carboxylic Acid |
| -COO- | 5. Ketone |
| C≡C | 6. Ester |
| -CO- | 7. Amide |
| -NH₂ | 8. Amine |
| -CONH₂ | 9. Alkyne |
Section B: Matching Functional Groups to Examples
Match each example compound in Column A with its functional group in Column B.
| Column A: Example Compound | Column B: Functional Group |
| CH₃CH₂OH | 1. Carboxylic Acid |
| CH₃COOH | 2. Alkene |
| CH₃CH₂NH₂ | 3. Aldehyde |
| CH₃OCH₃ | 4. Alcohol |
| CH₃CH₂CHO | 5. Amine |
| CH₃COCH₃ | 6. Ketone |
| H₂C=CH₂ | 7. Ester |
| CH₃COOCH₃ | 8. Ether |
Section C: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct answer for each question.
- Which of the following functional groups is present in carboxylic acids?
A) -OH
B) -CHO
C) -COOH
D) -CO- - Which functional group is found in alcohols?
A) -NH₂
B) -OH
C) -CHO
D) -COOH - Which of the following compounds contains a ketone functional group?
A) CH₃COCH₃
B) CH₃CH₂CHO
C) CH₃COOH
D) CH₃CH₂OH - What is the general formula of an ester?
A) RCOOH
B) ROR’
C) RCOOR’
D) RNH₂ - Which functional group is characteristic of aldehydes?
A) -CO-
B) -COOH
C) -CHO
D) -OH - Which of the following is an amine?
A) CH₃CH₂OH
B) CH₃COOCH₃
C) CH₃CH₂NH₂
D) CH₃COOH - What is the functional group present in ethers?
A) -COO-
B) -NH₂
C) -O-
D) -COOH
- Which functional group is present in alkynes?
A) -OH
B) C=C
C) -C≡C-
D) -CHO - Which compound contains an amide functional group?
A) CH₃CONH₂
B) CH₃COOCH₃
C) CH₃CH₂NH₂
D) CH₃CH₂OH - What is the correct name for CH₃CH₂COOH?
A) Ethanol
B) Propanoic acid
C) Propanal
D) Propanone
Answer Key
Section A: Functional Group Matching
1 → 3, 2 → 4, 3 → 1, 4 → 2, 5 → 6, 6 → 9, 7 → 5, 8 → 8, 9 → 7
Section B: Example Matching
CH₃CH₂OH → 4, CH₃COOH → 1, CH₃CH₂NH₂ → 5, CH₃OCH₃ → 8, CH₃CH₂CHO → 3, CH₃COCH₃ → 6, H₂C=CH₂ → 2, CH₃COOCH₃ → 7
Section C: MCQs
1 → C, 2 → B, 3 → A, 4 → C, 5 → C, 6 → C, 7 → C, 8 → C, 9 → A, 10 → B